The eye is a sensitive organ. It requires a consistent layer of moisture to ensure that it is comfortable and able to function optimally. Tears act as a lubricant to the eye. The tears not only keep the eyes moist but also wash away microorganisms and other debris that may cause damage or infection to the eye.
Dry eye syndrome is a condition characterized by the lack of sufficient moisture or lubricant on the eye surface. This is the result of not being able to produce adequate tears to provide lubrication to the eye. The eyes are therefore prone to constant irritation, inflammation and scarring.
Tears consist of oils produced in the eyelid’s Meibomian glands, water produced in the upper eyelid’s lacrimal glands and mucin produced in the conjunctiva’s goblet cells. Dry eye syndrome occurs when there is interference in the production of all or one of the components of tears. This results in instability and dryness of the eyes.
The category of dry eyes that an individual has is determined by tear components. Doctors determine the type of dry eye you are suffering from in order to establish an effective treatment to relieve the symptoms of your condition.
Symptoms of dry eye syndrome
Dry eye syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Itchy eyes
- Eye fatigue
- Eye soreness
- Heavy eyes
- Aching in and around the eyes
- Eye redness
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Gritty sensation
- Watery eyes
In addition to the symptoms listed above, dry eyes can result in inflammation. It can also result in damage to the eye surface that may have lasting effects.
Dry Eye Treatments
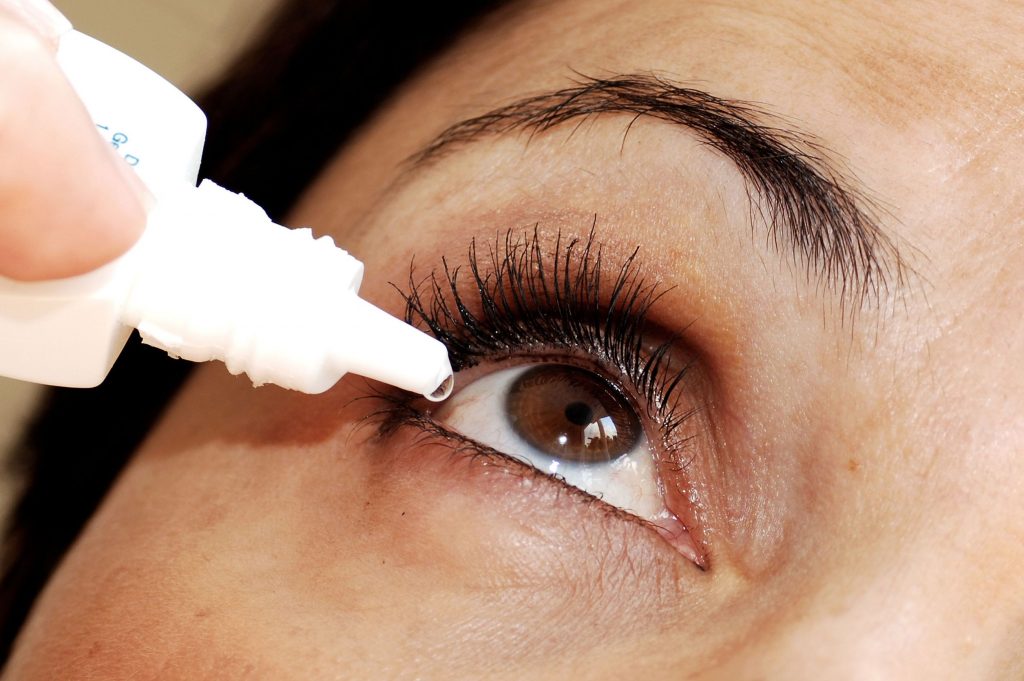
The most common treatments for dry eyes include the administration of artificial tears. Many doctors also recommend behavioral modifications in order to reduce the symptoms associated with dry eye. These modifications include staying clear of pets, taking frequent breaks when using computers and common eye hygiene.
In some cases, doctors may recommend medications or procedures to help increase the production of tears or decrease inflammation or irritation. These may include the administration of anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroid eye drops.
Serious cases that prove non responsive to the above treatments may require surgery. This includes Punctal occlusion, which involves the closing of the tear ducts to prevent tears from draining away from the eye and ensuring the eye remains moist. Salivary gland auto transplantation is often used as a last resort. It involves the removal of the saliva glands and replacing them under the skin that surrounds your eyes where they will act as a substitute to tears.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.